Every audit procedure obtains one or more types of evidence. The auditors goal is to obtain a sufficient amount of appropriate evidence at the lowest total cost. The next type of audit evidence that auditors can obtain is through observation. Comparing this data to 2016-17 in the year 2019-18 more than 34th of the companies in the list saw their fees increase by an average of 217 while a handful of 13rd companies saw their fees decrease by an average of. I Audit evidence is more reliable when it is obtained from independent sources outside the entity. According to Audit Analytics for the FTSE 350 Auditor Changes and Fees the following were the audit and audit related fees for FTSE 350 companies with auditor changes. Appropriateness of evidence is defined as the quality of evidence regarding their reliability as well as relevance for supporting the opinion of the auditor of the company. ISA 500 states that the responsibility of the auditor during an audit is to design and perform audit procedures in such a way to enable the auditor to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence to be able to draw reasonable conclusions on which to base the auditors opinion. Add the sales journal entries to determine whether they were correctly totaled. The following ï ve factors that inïuence the reliability of audit evidence are taken from ISA 500 Audit Evidence.
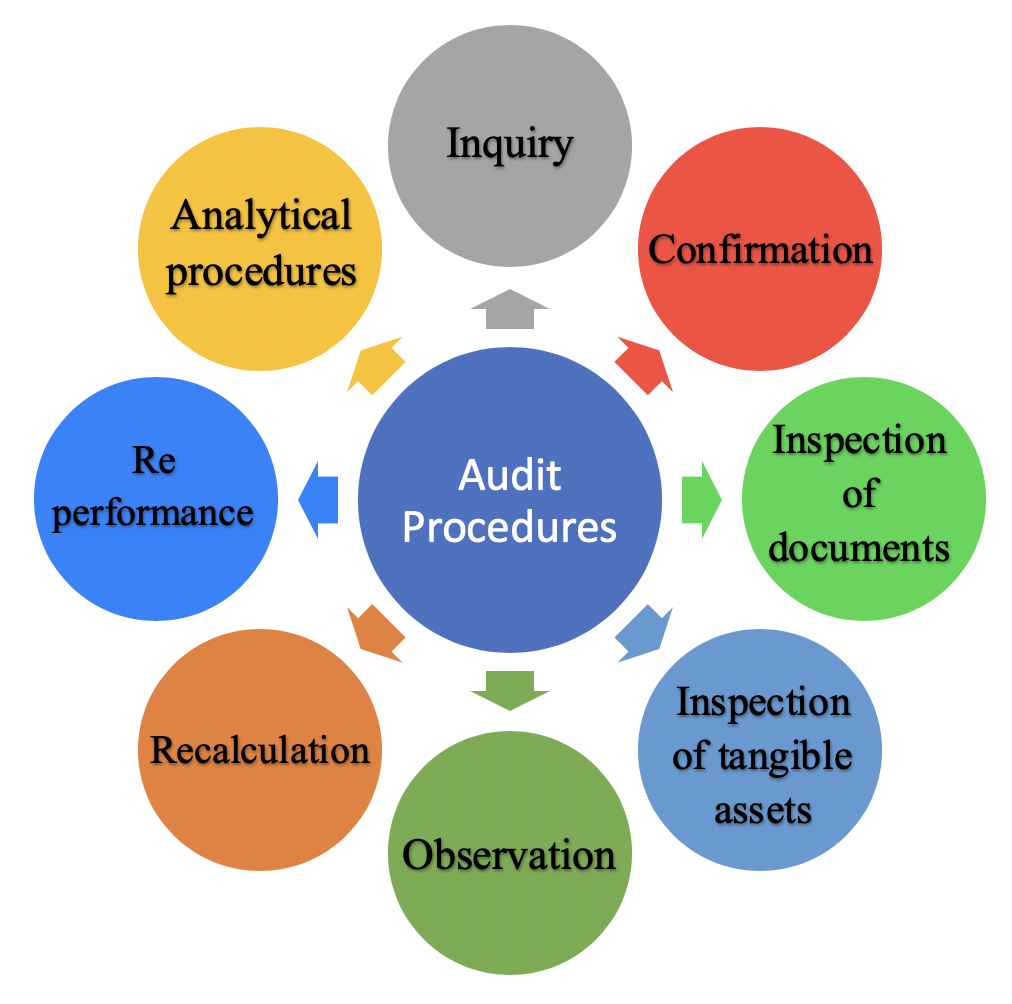
Ii Audit evidence that is generated internally is more reliable when the related controls imposed by the entity are effective. The next type of audit evidence that auditors can obtain is through observation. Auditors use audit evidence in many different forms and sources. Audit Documentation Auditing standards state that audit documentation is the principal record of auditing procedures applied evidence obtained and conclusions reached by the auditor in the engagement. Types of audit evidence. For an example of audit evidence. The following ï ve factors that inïuence the reliability of audit evidence are taken from ISA 500 Audit Evidence. Persuasiveness and Cost In making decisions about evidence for a given audit both persuasiveness and cost must be considered. The auditors goal is to obtain a sufficient amount of appropriate evidence at the lowest total cost. 1 physical examination 2 confirmation 3 inspection 4 analytical procedures 5 inquiries of the client 6 recalculation 7 reperformance and 8 observation.
It can help auditors get a view of the clients processes and analyze them for deficiencies. In observation auditors observe various aspects of the clients operations or processes. This type of evidence is most often associated with inventory and cash but is also applicable to the verification of securi- ties notes receivable and tangible capital assets. INSPECTION Inspection also called physical examination is the auditors inspec- tion or count of a tangible asset or document. According to Audit Analytics for the FTSE 350 Auditor Changes and Fees the following were the audit and audit related fees for FTSE 350 companies with auditor changes. Persuasiveness and Cost In making decisions about evidence for a given audit both persuasiveness and cost must be considered. 1 physical examination 2 confirmation 3 inspection 4 analytical procedures 5 inquiries of the client 6 recalculation 7 reperformance and 8 observation. Appropriateness of evidence is defined as the quality of evidence regarding their reliability as well as relevance for supporting the opinion of the auditor of the company. Every audit procedure obtains one or more types of evidence. Classify the item according to the eight types of audit evidence.
In observation auditors observe various aspects of the clients operations or processes. The auditors goal is to obtain a sufficient amount of appropriate evidence at the lowest total cost. I Audit evidence is more reliable when it is obtained from independent sources outside the entity. INSPECTION Inspection also called physical examination is the auditors inspec- tion or count of a tangible asset or document. According to Audit Analytics for the FTSE 350 Auditor Changes and Fees the following were the audit and audit related fees for FTSE 350 companies with auditor changes. This type of evidence is most often associated with inventory and cash but is also applicable to the verification of securi- ties notes receivable and tangible capital assets. Audit Documentation Auditing standards state that audit documentation is the principal record of auditing procedures applied evidence obtained and conclusions reached by the auditor in the engagement. Appropriateness of evidence is defined as the quality of evidence regarding their reliability as well as relevance for supporting the opinion of the auditor of the company. Ii Audit evidence that is generated internally is more reliable when the related controls imposed by the entity are effective. Inspecting could involve the use of physical evidence as do the procedures of counting.
I Audit evidence is more reliable when it is obtained from independent sources outside the entity. Documentation analytical procedures and re-performance are moderately costly. ISA 500 states that the responsibility of the auditor during an audit is to design and perform audit procedures in such a way to enable the auditor to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence to be able to draw reasonable conclusions on which to base the auditors opinion. The following ï ve factors that inïuence the reliability of audit evidence are taken from ISA 500 Audit Evidence. Audit evidence obtained directly by the auditor for example observa-tion of the application of a control is more reliable than audit evidence obtained indirectly or by inference for example inquiry about the ap-plication of a control. The amount and type of auditing evidence considered vary considerably based on the type of firm being audited as well as the required scope of the audit. Every audit procedure obtains one or more types of evidence. Add the sales journal entries to determine whether they were correctly totaled. Appropriateness of evidence is defined as the quality of evidence regarding their reliability as well as relevance for supporting the opinion of the auditor of the company. For an example of audit evidence.